Early music online is the result of a project aimed at digitizing 300 volumes of the world’s earliest printed music from holdings at the British Library and making them freely available online. The project has focused on the British Library’s holdings of 16th-century anthologies of printed music, as listed in RISM B/I (Recueils imprimés XVI-XVII siècles).
These collections printed in Italy, Germany, France, England, and Belgium contain approximately 10,000 works, which have been individually indexed. The volumes mainly comprise vocal polyphony partbooks, but they also include early printed tablatures for keyboard or plucked string instruments.
The digitized books can be browsed via Royal Holloway’s digital repository. Full details of each volume, searchable by composer and by title, with links to the digitized content, can also be found in the British Library Catalogue, UK RISM database, and COPAC.
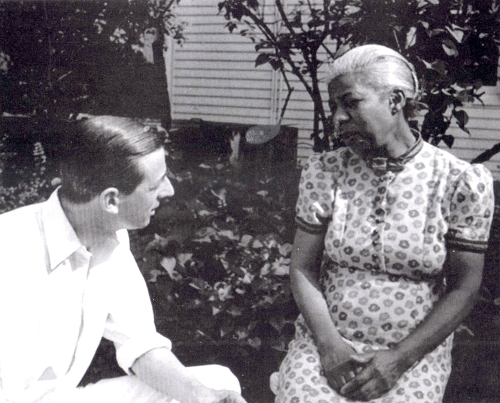
Above, an excerpt from a work by Jacob Clément (Clemens non Papa) in Le huitiesme livre des chansons a quatre parties, an anthology published in Antwerp by Tylman Susato in 1545 (click to enlarge). Below, Stile Antico sings Clemens’s Ego flos campi.
Related posts: