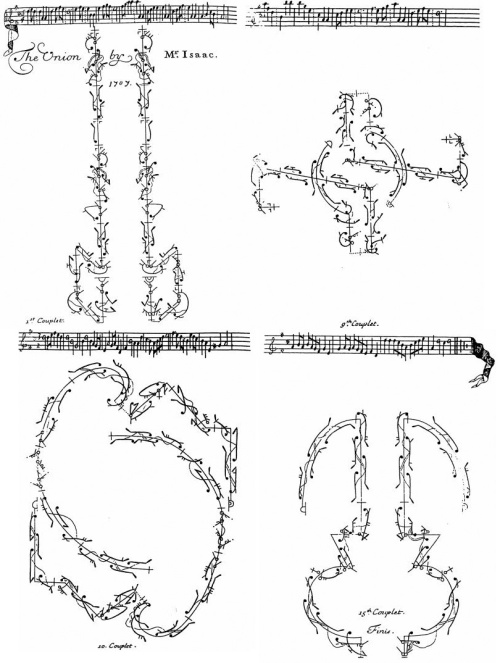
The celebrated late–17th- and early–18th-century English dancing master known in historical sources only as Mr. Isaac may have been Edward Isaac, who was baptized in 1643 and whose particulars fit in circumstantial ways with what little is known about the choreographer.
By the mid-1670s Mr. Isaac was well-connected in the court and theaters, and recognition of his work continually grew, lasting into the reign of George I. His extant dances, notated by John Weaver and others in the Beauchamp–Feuillet system, show a typically English love of formal complexity and occasional departures from fashionable French models, yet they share qualities that mark them as definitively his own.
This according to “Mr. Isaac, dancing-master” by Jennifer Thorp (Dance research XXIV/2 [Winter 2006] pp. 117–137).
Related article: Mr. Isaac and The Union